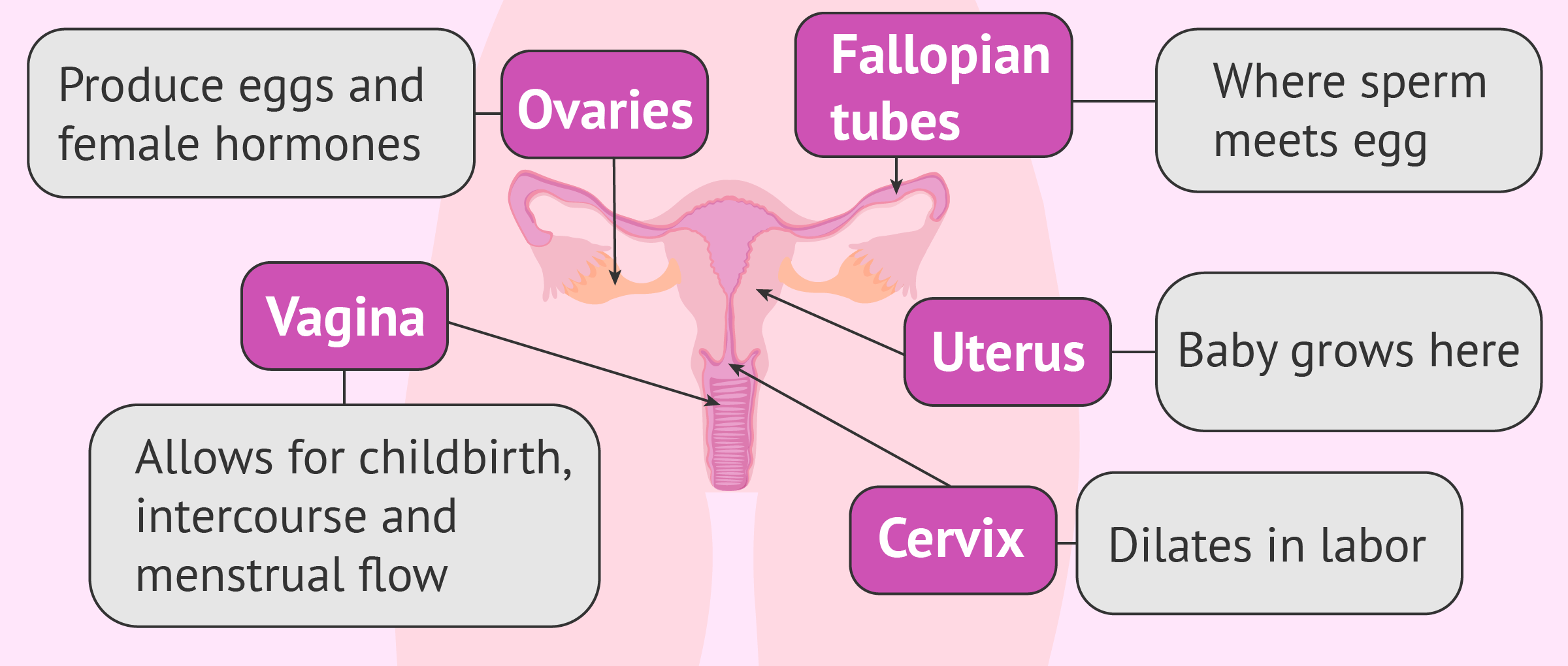
The uterus is a remarkable organ, primarily found in women's mammals, and plays a critical role in reproduction. It's a muscular organ located in the lower body, liable for nurturing a developing offspring during childbearing. Beyond childbirth, the matrix also expels its mucosa during the menstrual cycle, which is a natural process in a female's life. The shape is typically rounded, and the organ can dilate considerably to contain a developed baby.
Learning About Ovaries
The reproductive organs are vital components of the woman's reproductive framework, primarily liable for producing oocytes and hormones. Typically, women have two ovaries, situated on either side of the uterus. They play a significant part throughout a female's life, beginning with development during fetal periods and going through periods and possibly into menopause. Their complex functions are deeply linked with the broader health and condition of a woman.
Exploring Oviduct {Tubes
Oviduct channels are vital parts of the woman's procreative system, playing a crucial part in conception. They stretch from the matrix to the testicles, acting as a route for the ovum to travel from the testicle to the womb. Frequently, fertilization occurs within the isthmus, a defined section of the fallopian tube. Moreover, inflammation and blockage of these ducts can substantially affect fertility.
Keywords: vagina, vulva, anatomy, health, female, reproductive, intimate, hygiene, disorders, sexually transmitted infections, lubrication, childbirth, menstruation, pelvic floor, estrogen, pH balance, yeast infection, bacterial vaginosis, pelvic pain.
The Female Reproductive Opening
The vagina is a essential part of the female internal system, often confused with the vulva. It plays a key role in procreation, period flow, and sexual well-being. Proper maintenance is crucial for preventing problems like yeast infections, bacterial vaginosis, and addressing lower abdominal discomfort. Factors such as female hormones, internal environment and adequate natural fluids significantly impact the vagina's health. Awareness of sexually transmitted infections and their potential impact on the vagina is also extremely important for overall reproductive fitness. The strength of the muscles below the uterus is also important for childbirth.
The Vulva
The outer female reproductive structure encompasses the visible parts of the female genital region outside of the body. It's a complex region with several functions, including shielding the delicate structures and playing a role in sexual activity. Familiarizing oneself with its anatomy is vital for general well-being and sexual knowledge. This includes the labia, glans, and the opening which holds the discharge port and genital passage.
The Cervical Canal
The cervix, a important part of the reproductive anatomy, serves as a gateway between the uterus and the vaginal opening. Generally, it appears as a tight channel, about 2-3 centimeters in length, and plays a significant role in menstrual flow and childbirth. In pregnancy, the cervical canal stays sealed to protect the developing offspring, and then widens significantly to permit delivery. Its health is critical for procreative overall health.
Understanding the Labia Majora
The labia majora are an pair of large skin layers that constitute a component of the outer sexual area. Often, they mirror the pubic region, being made up of greasy substance and protected by hair growth, although this might vary widely among individuals. Acting as a important safeguarding shield, they help to shield the additional delicate elements underneath the vulva, also they add to the overall appearance and role of a women's body.
Delving into These Minora
Labia minora are a pair of small folds of flesh located immediately the vaginal opening. This area vary significantly for size, form, and color between women, often appear more pigmented than the surrounding skin. Despite this region lack a clear function in reproduction, they crucial for protection and the delicate vaginal structures. Changes in these dimensions or feel might sometimes indicate an medical issue, so it can be necessary to seek medical guidance if any issues develop.
Understanding The Clitoris
Many people consider the clitoris, a tiny organ located at the front of the vulva, to be the crucial area of sexual enjoyment. Distinct from other genital organs, it lacks a direct purpose in procreation; its only role is related to sexual response. The structure is remarkably sensitive, containing many of nerve endings, making it to provide intense feelings. More investigation continues to expand our comprehension of the complex anatomy and role.
- It is often called the third erotic zone.
- Several consider understanding of this clitoris is liberating.
Exploring Bartholin's Glands
Found on both side of the birth opening, Bartholin's glands|glands|structures play a relatively limited role in female reproductive function. Typically, they secrete a little amount of fluid|lubrication|moisture that aids with vaginal lubrication during sexual activity. Rarely, these glands|ducts|tubes can become blocked|clogged|swollen, leading to a tender cyst|swelling|mass and problem with walking. This condition, known as a Bartholin’s cyst, commonly necessitates medical attention.
Okay, here's the article paragraph adhering to your strict spintax and HTML requirements, focusing on Skene's Glands.
Exploring Skene's {Glands
Skene's ducts, also known as paraurethral ducts, are small tubes located near the urethra within the female's pelvis. These glands function similarly to the male prostate tissue, producing a liquid that helps lubrication and defense of the urethra. Despite these function isn't totally clear, research suggests these could play a role in female's sexual well-being. Some individuals may have discomforting problems related to the glands, leading to further research. In conclusion, Skene’s ducts represent an important but often overlooked aspect of woman’s anatomy.
Keywords: hymen, virginity, anatomy, female, membrane, health, misconception, folklore, cultural, biology, medical, intact, rupture, bleeding, hymenal, tissue, perception, history, examination, psychology.
The Hymeneal Tissue Explanation
The female membrane is a slight portion of mucus membrane located around the uterus in females. Often associated with virginity in traditional beliefs, it's importantly a aspect of girl’s biology. It’s important to appreciate that the hymen isn’t always unbroken, and its presence or absence doesn’t definitively indicate virginity. Many activities, including physical activity, tampon use, or even vigorous coughing, can cause a rupture of the female tissue. The often-discussed bleeding sometimes associated with hymenal tear is not but isn’t always occurring. Healthcare professionals can conduct an assessment of the hymeneal membrane, but its appearance shouldn’t be interpreted as a sole indicator of sexual history. There are many misconceptions surrounding the female tissue also it's critical to differentiate scientific data from folklore and emotional understandings.
Okay, here's an article paragraph on "Perineum" adhering to your incredibly specific instructions.
Exploring the Perineum
The area between the genitals is a fibrous region situated anterior to the anus and the vulva in individuals. The area plays the vital part in various physical activities, such as holding the abdominal organs and assisting in sensory feedback. Moreover, it experiences considerable stretching during vaginal delivery in women, that can cause temporary pain. Familiarity with the structure is thus important for medical professionals.
Understanding Your Body's Pelvic Floor
The pelvic floor is a group of fibers that stabilize your bladder and play a vital role in bodily well-being. It's generally overlooked, but improving your muscles can positively impact issues related to sexual health read more to balance. Conditions like incontinence or pressure can frequently can be alleviated with targeted pelvic floor exercises. It's beneficial understanding your pelvic area and how to support them healthy throughout your years.
The Birth Canal
The birth canal, also known as the introitus, is a fibromuscular passage extending from the vulva to the womb opening. It serves as the chief route for monthly flow, intimate intercourse, and labor and delivery. This distensible structure is lined with tissue and possesses unique folds, called rugae, which allow it to expand considerably. Its length varies among individuals, but typically measures around several inches in normal state. Health of the vagina is crucial for general health and comfort.
The Amazing Internal Layer (Endometrium)
The endometrium is a remarkably responsive tissue that undertakes a crucial role in female reproductive health . This innermost layer of the uterus sheds during menstruation if fertilization doesn’t happen , and it thickens each month in readiness for a potential lodging of a fertilized ovum . It’s made up of glandular and stroma cells, creating a specialized environment that constantly modifies throughout the reproductive cycle. Moreover , the endometrial depth and structure are significantly affected by chemical messengers , primarily estradiol and gestogen .
Understanding Ovarian Follicles
Female follicles are vital structures within the ovary, playing a key role in the development of oocytes and the regulation of the reproductive rhythm. Each female organ initially contains a considerable number of primordial follicles, which are small sacs containing immature oocytes. Throughout a woman's reproductive life, these follicles progress through different stages, some experiencing a maturation process, others remaining in a inactive state. The course of follicle growth involves sophisticated interactions between signals, including reproductive hormones and luteinizing hormone, which orchestrate the processes leading to ovulation.
Exploring Estrogen Binders
Estrogen receivers are cytoplasmic proteins found within multiple cell sorts throughout the structure. These significant entities act as controllers, binding to oestrogen agents and subsequently triggering a cascade of biological events. Essentially, when an oestrogen hormone attaches a binder, it promotes a structural modification that leads to different gene activity, influencing many processes, including maturation, breeding, and general health. The presence and amount of these receivers can differ significantly across areas, explaining the diverse effects of estrogen in the human structure.
Pregnancy Targets
Progesterone receptors, often abbreviated as PRs, are cytoplasmic proteins that mediate the effects of progesterone, a vital steroid chemical. These molecules belong the nuclear receptor superfamily and, upon binding with progesterone, undergo a conformational alteration leading to translocation to the nuclei and subsequent regulation of gene production. Two major types, PR-A and PR-B, exist due to alternative modification of the mRNA, each exhibiting subtly distinct influencing properties and tissue presence. Their function is essential in the maintenance of foalhood, the development of the milk-producing glands, and the regulation of the reproductive cycle in females. Dysregulation of pregnancy receptor communication has been associated in a number of fertility disorders.
Keywords: reproductive system, male reproductive system, female reproductive system, fertilization, hormones, ovaries, testes, uterus, sperm, egg, menstruation, puberty, pregnancy, contraception
The Genesis System
The our reproductive system is a fascinating network of structures responsible for procreation . It broadly splits into the male reproductive system and the female reproductive system, each with specialized functions. In males, the testes produce sperm, while in females, the ovaries release eggs. Fertilization, the joining of a sperm and an egg, can lead to pregnancy, a remarkable period of gestation . Hormones, like estrogen and testosterone, play a essential role in regulating development during puberty and throughout reproductive life. Menstruation is a periodic process in females, and contraception methods are obtainable to hinder unintended pregnancies. This wonderful system is crucial to the perpetuation of our species .